Head injuries can look harmless at first—but even a mild bump can turn serious within hours.
At Neurowellness Bangalore, we often see patients who delay care after a fall or accident, not realizing early warning signs of brain trauma.
Recognizing symptoms early can be the difference between full recovery and permanent damage.
Head Injury:

Head Injury is also known as Brain Injury or Traumatic Injury. If you are suffering from any symptoms after a head injury and looking for the best Brain Care Clinic in Bangalore, you are on the right page. Neuro Wellness is one of the best Brain Care in Jayanagar, Bangalore and Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah is one of the highly skilled best Neurosurgeon in Bangalore. So, let’s understand the causes and symptoms of head injury.
Causes of Head Injury –
Falls
Vehicle accidents
Sports Injuries
Violence
Explosive blasts and other combat injuries
Blast injury (Military actions)
Gunshot Wounds
Head Injury Symptoms –
There are two characteristics of head injury, Physical & Mental.
Physical Symptoms –
Tenacious headache or cerebral pain that deteriorates
Continued vomiting or nausea
Convulsions or seizures
Widening of one or both pupils of the eyes.
Clear liquids depleting from the nose or ears
Inability to awaken from sleep
Weakness or numbness in fingers and toes
Loss of coordination
Mental Symptoms –
Significant disarray
Agitation, aggressiveness, or another unusual way of behaving
Slurred speech
Coma and different problems of awareness
Children’s Symptoms –
Children are very different from adults in physiology and symptoms. Head injury can appear in children as well.
Children with head injuries might not be able to affect by headaches, sensory problems, confusion, and similar symptoms. Other symptoms are –
Change in eating or nursing propensities
Easy irritability
Persevering crying and powerlessness to be reassured
Change incapacity to pay attention
Change in sleep habits
Miserable or discouraged mood
Tiredness
Loss of interest in most loved toys or activities
Diagnosis –
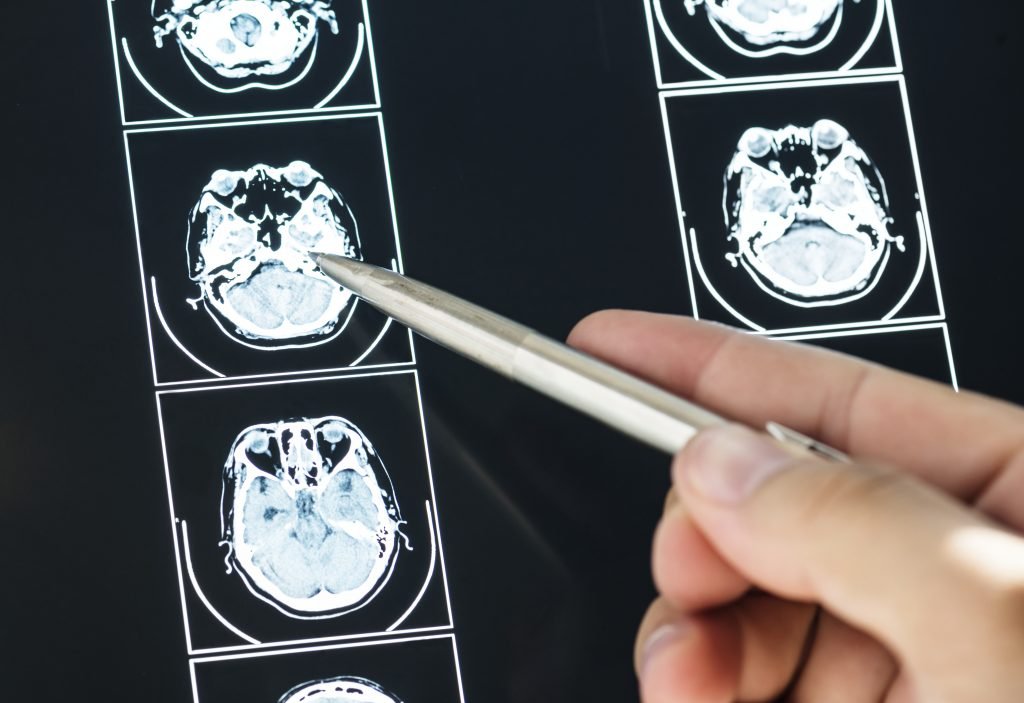
After the brain injury, the doctor may prescribe either MRI or CT scan depending on the patient’s condition.
Common Symptoms After a Head Injury
| Category | Symptoms | What to Do |
|---|---|---|
| Physical | Headache, vomiting, dizziness, blurred vision | Rest, avoid bright light, seek scan if persistent |
| Cognitive | Confusion, memory loss, delayed speech | Consult neurologist; avoid driving |
| Behavioral | Irritability, mood swings, fatigue | Monitor for 24 hrs; get evaluation |
| Severe | Loss of consciousness, seizures, clear fluid from nose/ears | Emergency → Visit ER immediately |

Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah
Consultant – Neurosurgeon, Neurointerventional Surgery, Spine Surgeon (Neuro)
23+ Years Experience Overall (17+ years as Neuro Specialist)
Available for Consultation: Jayanagar 9th Block & Kauvery Hospital, Electronic City
Conculsion
Emergency Brain Care at Neurowellness Bangalore
24×7 neuro-emergency, advanced CT/MRI imaging, and expert neurosurgeons led by Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah.
FAQs
1. Can mild head injuries cause brain damage?
Yes, repeated or untreated minor injuries can lead to long-term cognitive issues.
2. How long should I observe symptoms after a fall?
At least 48 hours. If new symptoms appear, seek immediate medical help.
3. Should children be monitored differently?
Yes. Children may not verbalize symptoms; watch for vomiting, irritability, or loss of balance.
4. How do AI tools help after head trauma?
AI systems analyze speech and motion patterns to detect subtle neurological changes for faster triage.

About Author
Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah
Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah, leading neurosurgeon and neurologist in Bangalore, has over 20 years of expertise in managing back pain, migraines, headaches, neuro disorders, and spine problems. His clinical excellence and patient-first approach make him one of the most trusted neuro doctors in Bangalore.
At Neurowellness Brain & Spine Clinic in Jayanagar and Kavery Hospital Electronic City, Dr. Ganesh provides comprehensive treatments ranging from minimally invasive spine surgery to advanced neurological care. As a respected back pain specialist and migraine doctor, he continues to deliver reliable outcomes for patients.
👉 Connect with Dr. Ganesh on LinkedIn

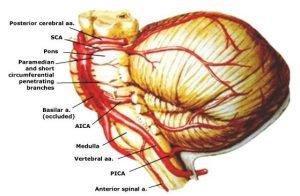
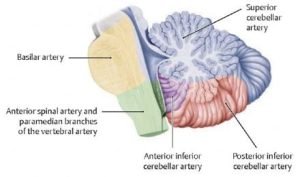




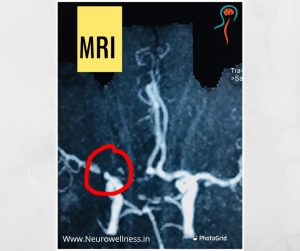
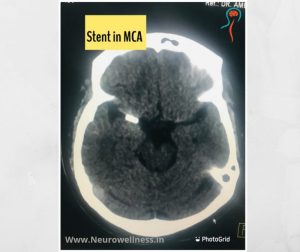
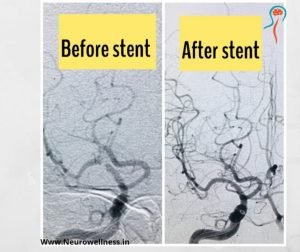
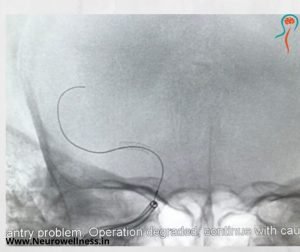
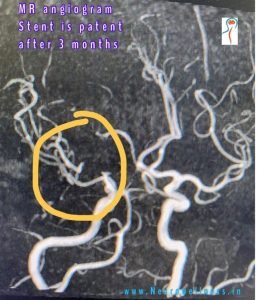














 A headache that gets worse even after you take pain medications so if you have an immediate health concern, don’t wait weeks to book an appointment with the best Headache Specialist in Bangalore.
A headache that gets worse even after you take pain medications so if you have an immediate health concern, don’t wait weeks to book an appointment with the best Headache Specialist in Bangalore.