What Is Pediatric Extradural Hematoma?
Pediatric extradural hematoma (EDH) is a life-threatening brain condition in which blood collects between the skull and the dura mater (outer covering of the brain), usually after head injury. This bleeding increases intracranial pressure and compresses the brain. Without immediate neurosurgical treatment, it can lead to brain herniation and sudden death.
It is one of the most surgically reversible brain emergencies — if diagnosed early.
Sudden Deterioration After Head Injury in a Child
A 7-year-old child was brought to our emergency department in Bengaluru after a two-wheeler accident while going to school.
Initially:
• Mild drowsiness
• No visible scalp injury
• No external bleeding
Within hours:
• She developed a seizure
• Became unconscious
• Slipped into deep coma
This was not a simple head injury. This was a life-threatening acute Extradural hematoma treatment in Bengaluru.
What Is Extradural Hematoma (EDH)?
An extradural hematoma is a collection of blood between the skull and the dura, usually caused by injury to the middle meningeal artery.
Common Causes:
• Road traffic accidents
• Two-wheeler accidents
• Falls in children
• Sports injuries
Why Is EDH Dangerous?
• Rapid rise in intracranial pressure
• Brain compression
• Brainstem herniation
• Sudden death if untreated
EDH is often referred to as a “talk and die” head injury because patients may initially appear stable before deteriorating rapidly.
Warning Signs of Serious Head Injury in Children
Parents must seek immediate medical evaluation if a child develops:
• Persistent drowsiness
• Vomiting after head injury
• Seizures
• Unequal pupils
• Decreased responsiveness
• Sudden unconsciousness
If any of these symptoms occur, an urgent CT scan of the brain is mandatory.
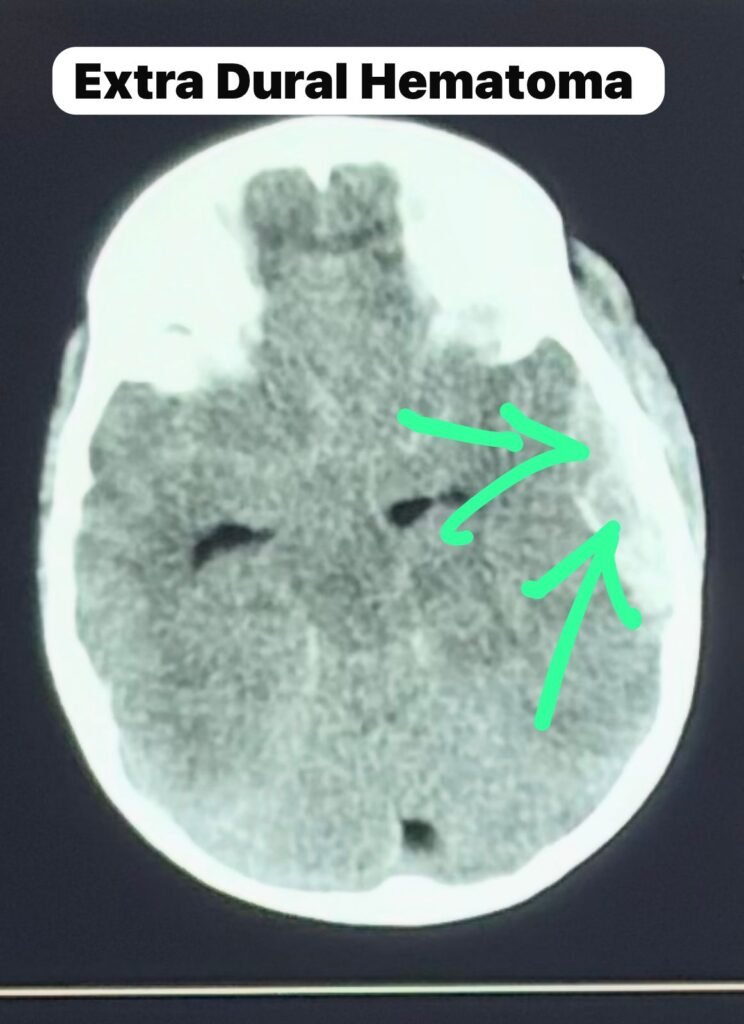
CT Scan Findings: A Surgical Emergency
The CT scan showed:
• Large left temporoparietal extradural hematoma
• Temporal bone fracture
• Significant midline shift
• Severe mass effect
The CT scan confirmed acute arterial EDH with impending brain herniation. Immediate neurosurgical intervention in Bengaluru was required.
Emergency Brain Surgery: Craniotomy and Evacuation
We performed an emergency left frontotemporal craniotomy to remove the blood clot.
Intraoperative Findings:
• Large extradural clot compressing the brain
• Brain initially non-pulsatile
• Active bleeding from middle meningeal artery
• Hemostasis achieved
• Bone flap replaced
Once pressure was relieved, the brain began pulsating normally — a crucial turning point.

Postoperative Recovery: From Coma to Consciousness
Postoperative CT scan showed:
• Complete evacuation
• Resolution of midline shift
• Relaxed brain
Clinical improvement:
• Eye opening
• Limb movements
• Extubated next day
• Started oral feeds
A potentially fatal brain injury was reversed because of timely diagnosis and Emergency brain surgery in Electronic City.
Why Early CT Scan and Neurosurgeon Consultation Is Critical
Many parents assume that absence of external wound means no serious injury. That is not true.
• Skull may fracture without visible injury
• Arterial bleeding can progress silently
• Neurological deterioration can be sudden
Time is brain. Delay can lead to irreversible damage.
If both pupils become fixed and dilated, even surgery may not save the brain.
Emergency Neurosurgery in Bengaluru – When Minutes Matter
Successful outcomes depend on:
• 24/7 CT scan availability
• Dedicated neuro ICU
• Immediate operating room access
• Advanced Pediatric neurosurgery Bengaluru
Early referral to a tertiary care center can be life-saving.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Can a child have brain bleeding without scalp injury?
Yes. Extradural hematoma can occur even if the skin appears normal.
2. How fast can extradural hematoma become dangerous?
It can progress within minutes to hours.
3. Is surgery always required for EDH?
Large EDH with neurological deterioration requires emergency craniotomy.
4. Can children fully recover after EDH surgery?
Yes, if treated early before brainstem compression occurs.
5. When should I consult a neurosurgeon after head injury?
Immediately if there is drowsiness, vomiting, seizures, unequal pupils, or altered consciousness.
Pediatric Head Injury & Emergency Brain Surgery Consultation in Bengaluru
Dr. Ganesh Veerabhadraiah is a highly experienced Neurosurgeon and the Head of Department (HOD) & Consultant Neurosurgeon at Kauvery Hospital. He specializes in pediatric neurosurgery, brain trauma management, emergency brain surgery, and complex cranial procedures.
With extensive experience in treating life-threatening brain conditions such as pediatric extradural hematoma, traumatic brain injuries, brain tumors, and intracranial hemorrhages, Dr. Ganesh is known for his prompt decision-making in critical neurosurgical emergencies.
Conclusion
Pediatric extradural hematoma is one of the most surgically reversible brain emergencies if diagnosed in time.
Early CT scan.
Rapid referral.
Immediate neurosurgical intervention.
Advanced ICU care.
Head injury in children must never be ignored.
Prompt evaluation and expert treatment can make the difference between life and death.

